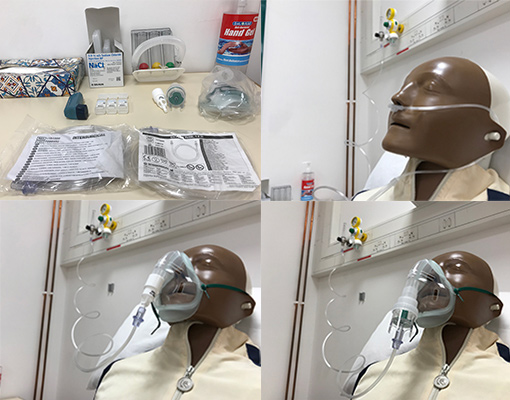
Test preparation
The test is designed to reflect the nature of the syllabus and knowledge required for a pre-registration programme in the Republic of Ireland as per the NMBI standards and requirements.
The test addresses the NMBI domains of competency for the pre-registration programme in an attempt to ensure patient safety and public protection. The domains of competency and indicative content of the NMBI requirements and standards must be fully and carefully considered in order to help guide your revision for the test.
In your revision, based on the NMBI standards and requirements, multiple sources should be considered including your notes and textbooks from your own training but be sure to use the most up-to-date research-based sources. Essential minimum background reading is detailed below. All of the references below will be included throughout the OSCE stations. Before presenting for the test, an applicant must know how to complete and interpret/analyse each piece of documentation as included below.
Please note: RCSI does not approve or acknowledge any preparation or review sessions/courses/programmes for the test.
In preparation for the test, it is essential that you base your revision on the NMBI publication: NMBI Standards and Requirements for Nurse Registration Education Programmes (fifth edition).
Please note: You are encouraged to check this webpage on a regular basis for additions and updates regarding revision and preparation.